Hepatitis B Therapy
However HBV replication may chronically persist in the liver 16 even in patients with anti-HBs for several years after acute hepatitis B. Combined hepatitis B diphtheria tetanus acellular pertussis DTaP and inactivated poliovirus IPV vaccine.

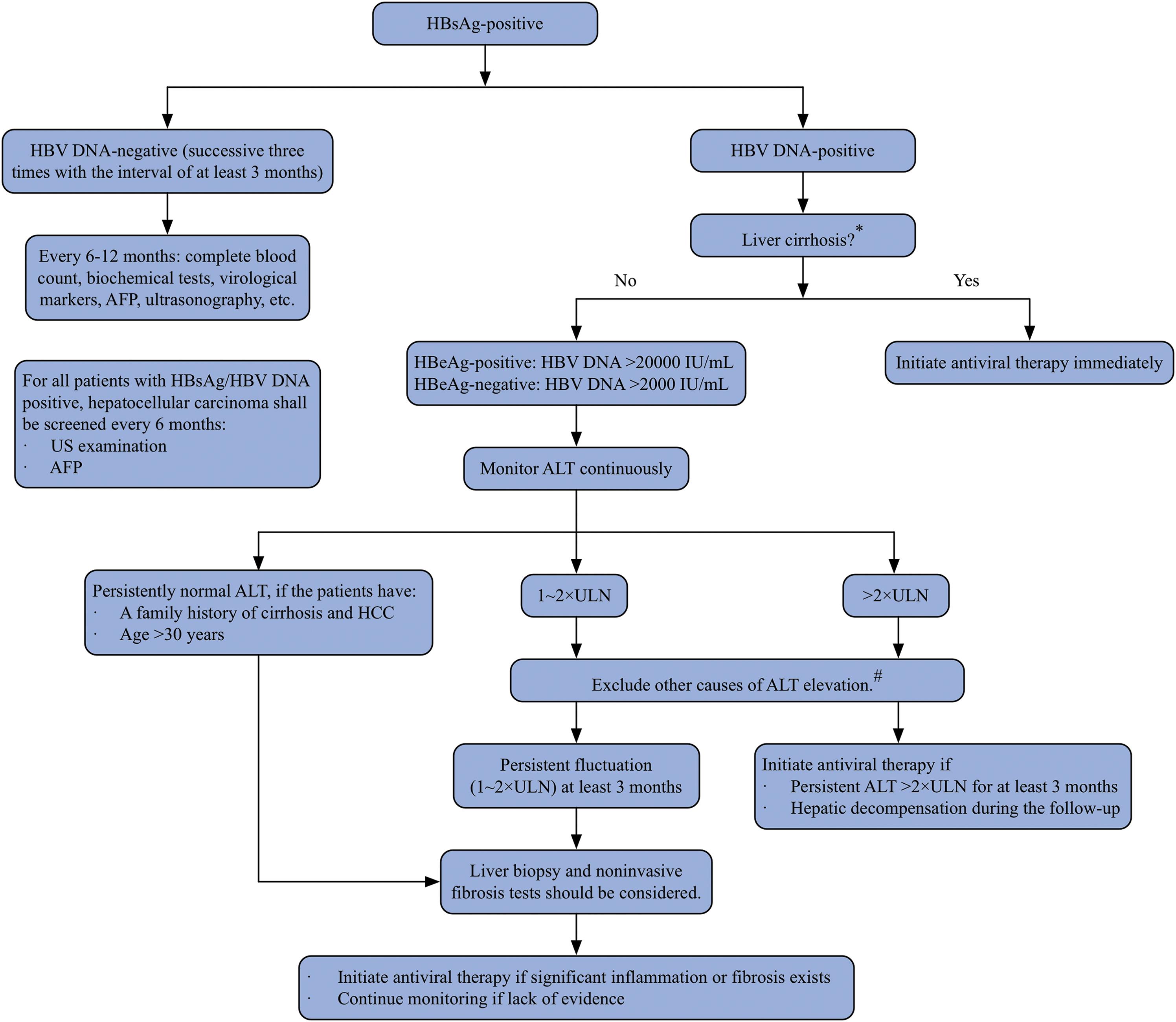
Virtual Surveillance Pathway For Hepatitis B Hbv Patients The British Society Of Gastroenterology
Short-term acute hepatitis B does not usually need specific treatment but may require treatment to relieve the symptoms.
Hepatitis b therapy. The goals of novel therapies for chronic hepatitis B are to cure the chronic infection and thereby prevent complications of chronic liver disease cirrhosis HCC and liver-related death. Use of antiviral prophylaxis might be warranted in patients who test positive for hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg particularly those with quantifiable HBV DNA. The selection of a potent nucleostide analogue with a high barrier to resistance as a first-line therapy such as entecavir or tenofovir provides the best chance of achieving long-term treatment goals and should be used wherever possible.
Unlike pre-vious AASLD practice guidelines this guideline was developed in compliance with the Institute of Medicine standards for trustworthy practice guidelines and uses the Grading of Recommendation Assessment Development. In clinical practice treatment response is determined by suppression of serum HBV DNA levels. In clinical practice treatment response is determined by suppression of.
The most common of these specific circumstances are listed below. 1-4 These agents commonly used in the treatment of B-cell malignancies such as B-celldepleting antibodies anthracycline derivatives high-dose corticosteroids immune checkpoint inhibitors tyrosine-kinase inhibitors and antimetabolites are associated with varied risks of HBV. The drug can also cause high blood pressure and bleeding problems.
It is important to appreciate that any definition of a cure should encompass eradication of the chronic viral infection as well as resolution of the underlying liver disease. Hepatitis B virus HBV reactivation typically occurs in patients with B-cell malignancies and concomitant HBV infection after exposure to immunosuppressive or cytotoxic agents. The choice of hepatitis B therapy in these patients depends on the management of the patients HIV.
The goal of hepatitis B treatment is to prevent cirrhosis liver decompensation and hepatocellular carcinoma. Ad HCPs - Read About a Treatment for Hep B How it May Help Your Patients. Ad HCPs - Read About a Treatment for Hep B How it May Help Your Patients.
Hepatitis B vaccine is part of routine immunizations in the United States and as a result the incidence of HBV has declined8 Table 2 lists hepatitis B vaccines and recommended dosing schedules. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus HBV could be fatal in the patients with hepatitis B infection and chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy. Hepatitis B therapy Hellan Kwon and Anna S.
For those patients not being treated or on stable regimens of highly active antiretroviral therapy HAART pegylated-interferon alfa if the CD4 count is 500 cellsmm 3 adefovir or entecavir can be administered. The new therapeutic approach is based on shutting down the viral hepatitis B genome located in the nucleus of infected liver cells. As current treatment options almost never achieve eradication of hepatitis B virus HBV the most realistic goal for HBV treatment is persistent inhibition of viral replication and ALT normalization.
Long-term chronic hepatitis B is often treated with medication to keep the virus under control. Thus the decision to start treatment should be based on careful patient selection and individualized decisions. We review the risk of HBV reactivation screening of HBV infection and the strategies of prophylaxis of HBV reactivation in patients requiring chemotherapy and immunosuppressive therapy.
Profound durable therapeutic HBV DNA suppression to slow and reverse the. Combined Hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine. There are a variety of special clinical situations in patients with hepatitis B where antiviral therapy may be warranted regardless of cirrhosis status hepatic aminotransferase levels or HBV DNA levels.
ENGERIX-B RECOMBIVAX HB HEPLISAV-B Combination vaccines. Side effects of targeted oral therapy with sorafenib include nausea vomiting mouth sores and loss of appetite. Antiviral drug resistance is a crucial factor that frequently determines the success of long-term therapy for chronic hepatitis B.
Cannot be administered before age 6 weeks or after age 7 years. More effective and less resistance-prone antiviral agents are now available to treat hepatitis B virus HBV infection. AASLD on the treatment of chronic hepatitis B CHB virus HBV infection in adults and children.
In clinical practice treatment response is determined by suppression of serum HBV DNA levels hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion to hepatitis B e antibody hepatitis B surface antigen los. Sometimes a person may have chest pain bleeding problems or blisters on the hands or feet. HBV reactivation occurs frequently in patients with chronic HBV and HCV coinfection receiving DAA therapy but is rare among patients with resolved HBV infection.
Because HBV covalently closed circular DNA remains present in hepatocytes and provides a stable template for replication of HBV viral reactivation has been reported after immunosuppressive therapy. Emergency treatment can also be given soon after possible exposure to the hepatitis B virus to stop an infection developing. Lok Abstract The goal of hepatitis B treatment is to prevent cirrhosis liver decompensation and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Single-antigen hepatitis B vaccines. Most cases of acute hepatitis B completely resolve in adult patients who become seronegative for HBsAg but seropositive for anti-HBc andor anti-HBs. The goal of hepatitis B treatment is to prevent cirrhosis liver decompensation and hepatocellular carcinoma.
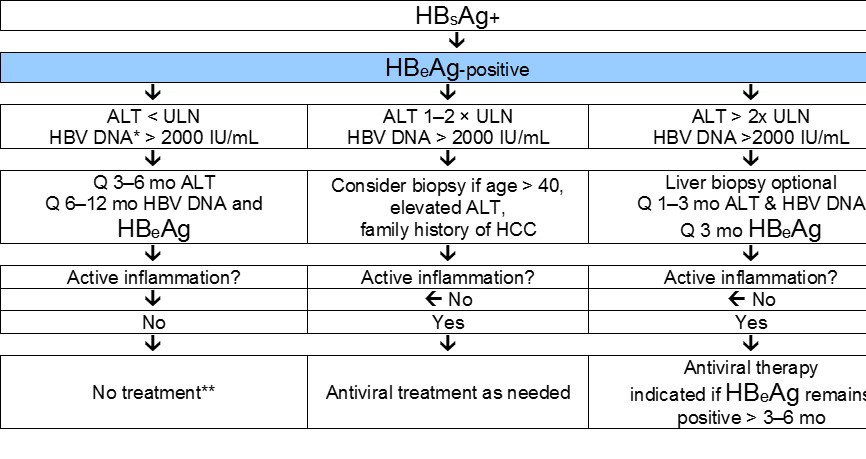
English World Gastroenterology Organisation
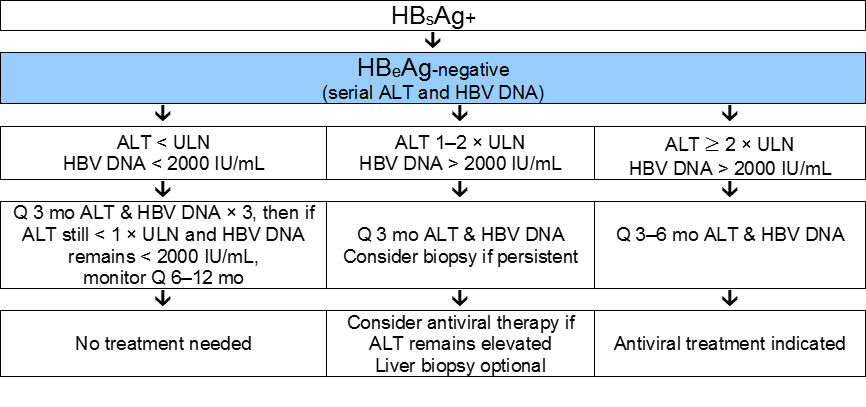
English World Gastroenterology Organisation
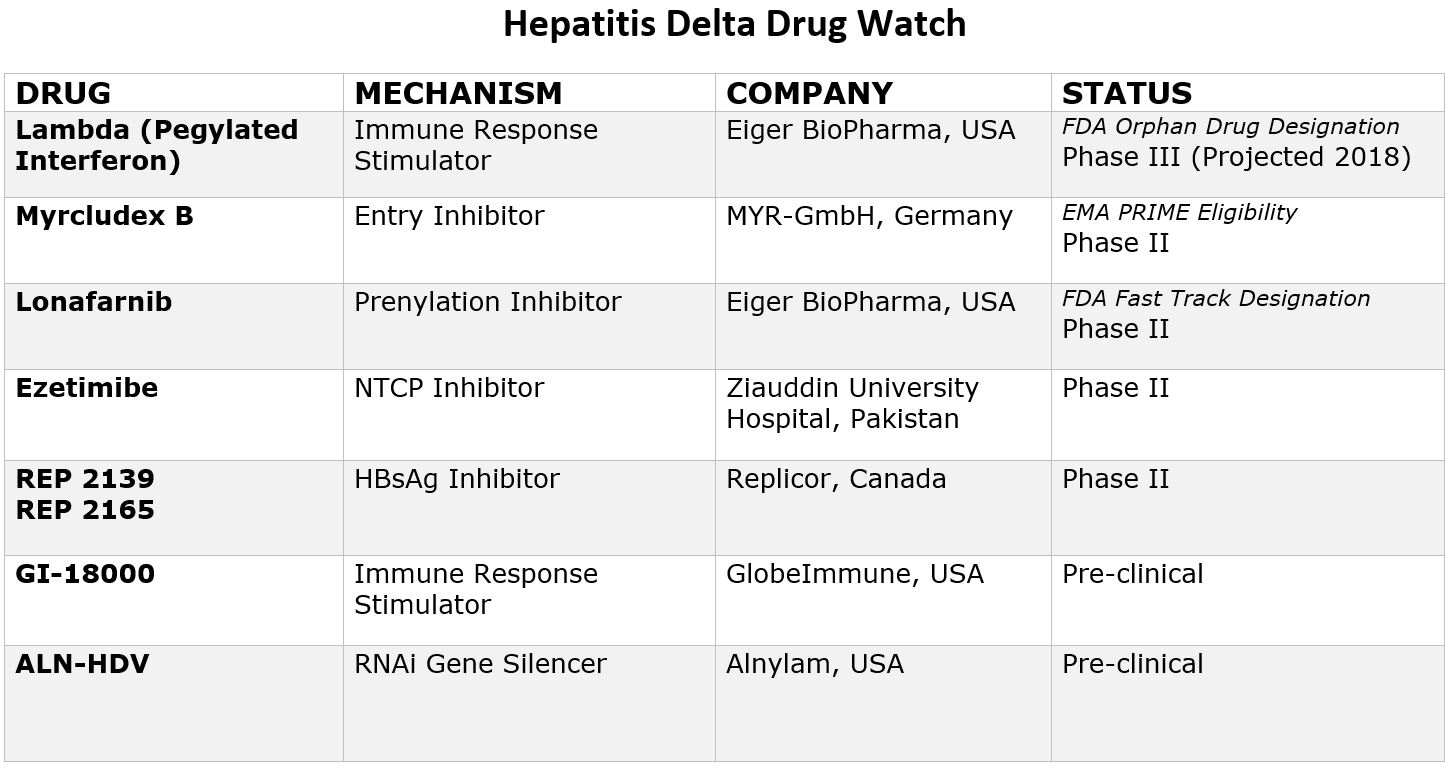
What New Treatments Are On The Horizon For Hepatitis B D Coinfected Patients Hepatitis B Foundation

Hepatitis B Related Outcomes Following Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy In Taiwanese Patients With Chronic Hbv Hcv Co Infection Journal Of Hepatology

Guideline Of Prevention And Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B 2015 Update
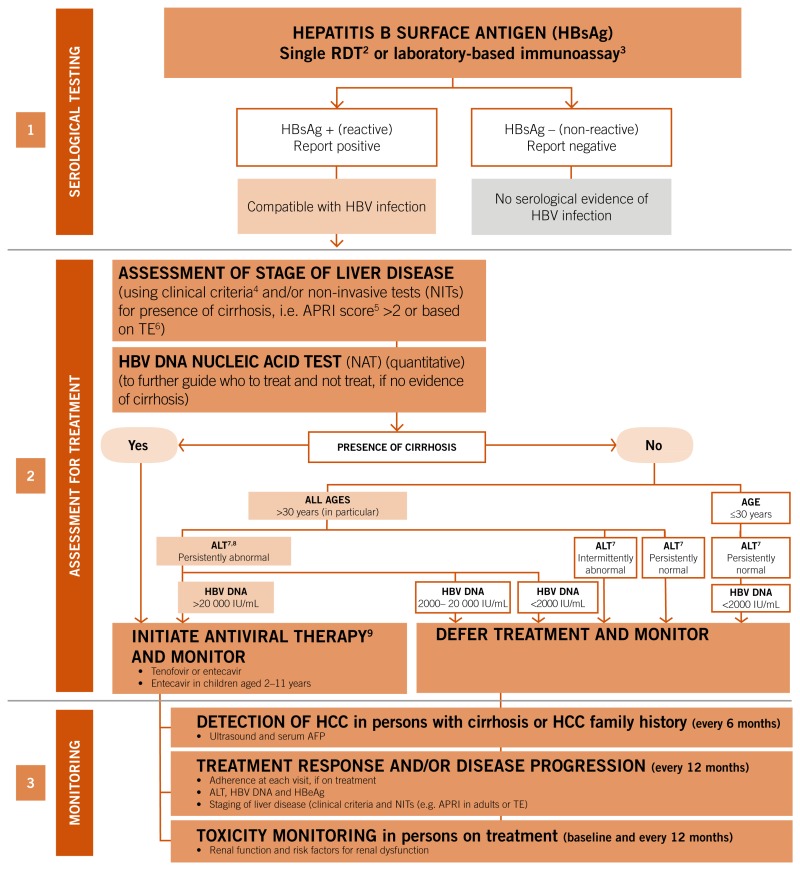
Fig 2 Summary Algorithm For Diagnosis Treatment And Monitoring1 Of Chronic Hbv Infection Who Guidelines On Hepatitis B And C Testing Ncbi Bookshelf
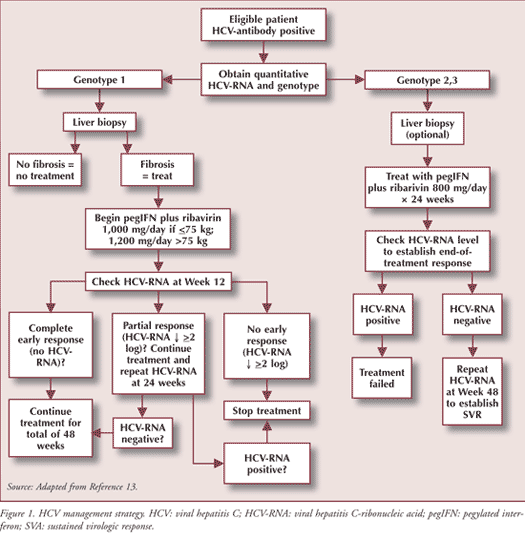
Overview Of Hepatitis B And C Management

Hepatitis B Related Outcomes Following Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy In Taiwanese Patients With Chronic Hbv Hcv Co Infection Journal Of Hepatology
New Approach For Potential Treatment Of Liver Eurekalert

Fda Approved Drugs For The Treatment Of Chronic Hbv Infection 3 Download Table

Treatment Of Hepatitis B World Hepatitis Day Infographics Vector Illustration On Isolated Background Stock Vector Illustration Of Care Biology 151220638

Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection The Lancet

Posting Komentar untuk "Hepatitis B Therapy"